


Siguiente: Símbolos, Métodos y Procs Subir: Programación Funcional Anterior: Aplicación Parcial de Funciones Índice General Índice de Materias
La memoizacion es una técnica que se usa para acelerar el cómputo de una función cuando:
En esta sección aumentamos el módulo Functional con el operador unario
+lambda
que retorna una lambda equivalente a su argumento
pero que cachea la relación entre argumentos y el valor retornado.
Veamos un ejemplo de uso. Las circustancias enumeradas anteriormente se dan en el cálculo de la función de Fibonacci.
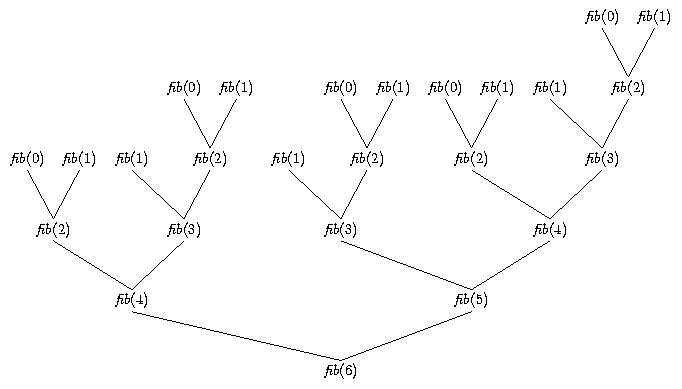
Arbol de llamadas para la función de Fibonacci
require './functional_partial'
require 'benchmark'
....
if $0 == __FILE__
fib = lambda { |n| n < 2 ? n : fib[n-1] + fib[n-2] }
fibm = +fib
n = 35
Benchmark.benchmark(CAPTION, 7, FORMAT) do |x|
tf = x.report("computed:") { fib[n] }
tt = x.report("memoized:") { fibm[n] }
end
end
La ejecución compara las dos versiones, con y sin memoizar:
[~/TheRubyProgrammingLanguage/Chapter6MethodsProcsLambdasAndClosures]$ ruby functional_memoize.rb
user system total real
computed: 6.500000 0.010000 6.510000 ( 6.520144)
memoized: 6.140000 0.000000 6.140000 ( 6.153518)
Este es el código de memoize:
[~/TheRubyProgrammingLanguage/Chapter6MethodsProcsLambdasAndClosures]$ cat functional_memoize.rb
require './functional_partial'
require 'benchmark'
include Benchmark
module Functional
#
# Return a new lambda that caches the results of this function and
# only calls the function when new arguments are supplied.
#
def memoize
cache = {} # An empty cache. The lambda captures this in its closure.
lambda {|*args|
# notice that the hash key is the entire array of arguments!
cache[args] = self[*args] unless cache.has_key?(args)
cache[args]
}
end
alias +@ memoize # cached_f = +f
end
(caption = "", label_width = nil, format = nil, *labels)
Benchmark::Report object, which may be
used to collect and report on the results of individual benchmark
tests.
label_width leading spaces for labels on each line.
caption at the top of the report, and uses format to format
each line.
Casiano Rodriguez León 2015-01-07