


Siguiente: Creando un ORM Subir: Lenguajes de Dominio Específico. Anterior: Un DSL para Procesar Índice General Índice de Materias
HTMLForm.generate(STDOUT) do
comment "This is a simple HTML form"
form :name => "registration",
:action => "http://www.example.com/register.cgi" do
content "Name:"
br
input :name => "name"
br
content "Post:"
br
textarea :name => "address", :rows=>6, :cols=>40 do
"Please enter your post here" # Este bloque retorna contenido
end
br
button { "Submit" } # Este bloque retorna contenido
end
end
[xmlgenerator]$ ruby xml_generator.rb > ejemplo.html
[xmlgenerator]$ cat ejemplo.html <!-- This is a simple HTML form --> <form name='registration' action='http://www.example.com/register.cgi' method='GET' enctype='application/x-www-form-urlencoded'>Name:<br/> <input name='name' type='text'/> <br/> Post:<br/> <textarea name='address' rows='6' cols='40'>Please enter your post here</textarea> <br/> <button type='submit'>Submit</button> </form>
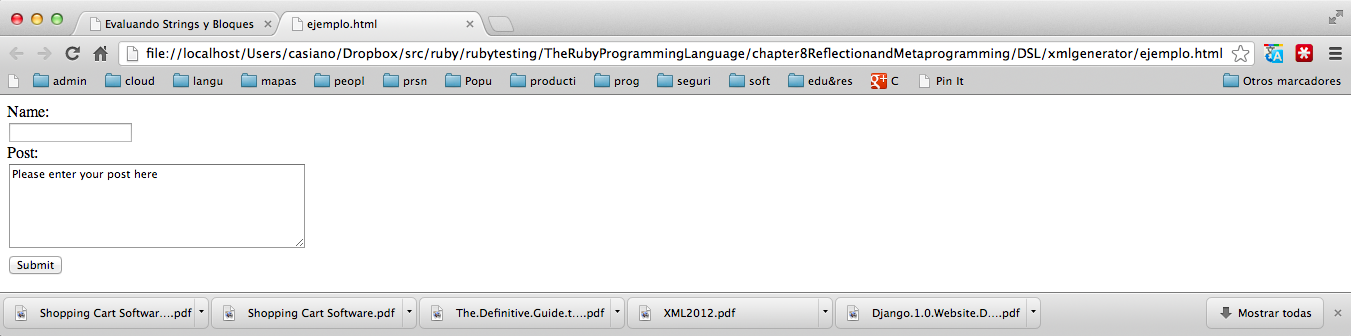
Este DSL permite describir una gramática XML:
Que tags son permitidos y para cada tag que atributos son legales y de que tipo son. Se usaría así:
class HTMLForm < XMLGrammar
element :form, :action => REQ, # atributo requerido
:method => "GET", # cadena: valor por defecto
:enctype => "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
:name => OPT # opcional
element :input, :type => "text", :name => OPT, :value => OPT,
:maxlength => OPT, :size => OPT, :src => OPT,
:checked => BOOL, :disabled => BOOL, :readonly => BOOL
element :textarea, :rows => REQ, :cols => REQ, :name => OPT,
:disabled => BOOL, :readonly => BOOL
element :button, :name => OPT, :value => OPT,
:type => "submit", :disabled => OPT
element :br
end
El método element es proveído por
XMLGrammar y
construye un método de instancia
con el nombre especificado (por ejemplo, :form) como primer
argumento en la subclase (HTMLForm en el ejemplo).
Como segundo argumento opcional recibe un hash especificando los atributos
legales del elemento y de que tipo son (REQ por requerido, OPT por opcional,
una String como en :method => "GET" indica valor por defecto y BOOL para atributos
cuyo valor es su propio nombre.
En el código anterior se crean métodos form, input, texarea, button
y br en la clase HTMLForm.
class XMLGrammar
# Create an instance of this class, specifying a stream or object to
# hold the output. This can be any object that responds to <<(String).
def initialize(out)
@out = out # Remember where to send our output
end
# Invoke the block in an instance that outputs to the specified stream.
def self.generate(out, &block)
new(out).instance_eval(&block)
end
# Define an allowed element (or tag) in the grammar.
# This class method is the grammar-specification DSL
# and defines the methods that constitute the XML-output DSL.
def self.element(tagname, attributes={})
@allowed_attributes ||= {}
@allowed_attributes[tagname] = attributes
class_eval %Q{
def #{tagname}(attributes={}, &block)
tag(:#{tagname},attributes,&block)
end
}
end
# These are constants used when defining attribute values.
OPT = :opt # for optional attributes
REQ = :req # for required attributes
BOOL = :bool # for attributes whose value is their own name
def self.allowed_attributes
@allowed_attributes
end
# Output the specified object as CDATA, return nil.
def content(text)
@out << text.to_s
nil
end
# Output the specified object as a comment, return nil.
def comment(text)
@out << "<!-- #{text} -->\n"
nil
end
# Output a tag with the specified name and attribute.
# If there is a block, invoke it to output or return content.
# Return nil.
def tag(tagname, attributes={})
# Output the tag name
@out << "<#{tagname}"
# Get the allowed attributes for this tag.
allowed = self.class.allowed_attributes[tagname]
# First, make sure that each of the attributes is allowed.
# Assuming they are allowed, output all of the specified ones.
attributes.each_pair do |key,value|
raise "unknown attribute: #{key}" unless allowed.include?(key)
@out << " #{key}='#{value}'"
end
# Now look through the allowed attributes, checking for
# required attributes that were omitted and for attributes with
# default values that we can output.
allowed.each_pair do |key,value|
# If this attribute was already output, do nothing.
next if attributes.has_key? key
if (value == REQ)
raise "required attribute '#{key}' missing in <#{tagname}>"
elsif value.is_a? String
@out << " #{key}='#{value}'"
end
end
if block_given?
# This block has content
@out << '>' # End the opening tag
content = yield # Invoke the block to output or return content
if content # If any content returned
@out << content.to_s # Output it as a string
end
@out << "</#{tagname}>\n" # Close the tag
else
# Otherwise, this is an empty tag, so just close it.
@out << "/>\n"
end
nil # Tags output themselves, so they don't return any content.
end
end
[~/chapter8ReflectionandMetaprogramming/DSL/xmlgenerator(master)]$ pwd -P /Users/casiano/Google Drive/src/ruby/TheRubyProgrammingLanguage/chapter8ReflectionandMetaprogramming/DSL/xmlgenerator
class XMLGrammar
# Create an instance of this class, specifying a stream or object to
# hold the output. This can be any object that responds to <<(String).
def initialize(out)
@out = out # Remember where to send our output
end
# Invoke the block in an instance that outputs to the specified stream.
def self.generate(out, &block)
new(out).instance_eval(&block)
end
# Define an allowed element (or tag) in the grammar.
# This class method is the grammar-specification DSL
# and defines the methods that constitute the XML-output DSL.
def self.element(tagname, attributes={})
@allowed_attributes ||= {}
@allowed_attributes[tagname] = attributes
class_eval %Q{
def #{tagname}(attributes={}, &block)
tag(:#{tagname},attributes,&block)
end
}
end
# These are constants used when defining attribute values.
OPT = :opt # for optional attributes
REQ = :req # for required attributes
BOOL = :bool # for attributes whose value is their own name
def self.allowed_attributes
@allowed_attributes
end
# Output the specified object as CDATA, return nil.
def content(text)
@out << text.to_s
nil
end
# Output the specified object as a comment, return nil.
def comment(text)
@out << "<!-- #{text} -->\n"
nil
end
# Output a tag with the specified name and attribute.
# If there is a block, invoke it to output or return content.
# Return nil.
def tag(tagname, attributes={})
# Output the tag name
@out << "<#{tagname}"
# Get the allowed attributes for this tag.
allowed = self.class.allowed_attributes[tagname]
# First, make sure that each of the attributes is allowed.
# Assuming they are allowed, output all of the specified ones.
attributes.each_pair do |key,value|
raise "unknown attribute: #{key}" unless allowed.include?(key)
@out << " #{key}='#{value}'"
end
# Now look through the allowed attributes, checking for
# required attributes that were omitted and for attributes with
# default values that we can output.
allowed.each_pair do |key,value|
# If this attribute was already output, do nothing.
next if attributes.has_key? key
if (value == REQ)
raise "required attribute '#{key}' missing in <#{tagname}>"
elsif value.is_a? String
@out << " #{key}='#{value}'"
end
end
if block_given?
# This block has content
@out << '>' # End the opening tag
content = yield # Invoke the block to output or return content
if content # If any content returned
@out << content.to_s # Output it as a string
end
@out << "</#{tagname}>\n" # Close the tag
else
# Otherwise, this is an empty tag, so just close it.
@out << "/>\n"
end
nil # Tags output themselves, so they don't return any content.
end
end
class HTMLForm < XMLGrammar
element :form, :action => REQ,
:method => "GET",
:enctype => "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
:name => OPT
element :input, :type => "text", :name => OPT, :value => OPT,
:maxlength => OPT, :size => OPT, :src => OPT,
:checked => BOOL, :disabled => BOOL, :readonly => BOOL
element :textarea, :rows => REQ, :cols => REQ, :name => OPT,
:disabled => BOOL, :readonly => BOOL
element :button, :name => OPT, :value => OPT,
:type => "submit", :disabled => OPT
element :br
end
HTMLForm.generate(STDOUT) do
comment "This is a simple HTML form"
form :name => "registration",
:action => "http://www.example.com/register.cgi" do
content "Name:"
br
input :name => "name"
br
content "Post:"
br
textarea :name => "address", :rows=>6, :cols=>40 do
"Please enter your post here"
end
br
button { "Submit" }
end
end
Casiano Rodriguez León 2015-01-07