


Siguiente: Local Git Repos Subir: Creando Gemas y Publicándolas Anterior: Optimistic and Pessimistic Version Índice General Índice de Materias
bundle outdated to print a list of gems that could be upgraded.
If you want to upgrade a specific gem, run
bundle update GEMor run
bundle updateto update everything. After the update finishes, make sure all your tests pass before you commit your new
Gemfile.lock!
bundle update won't just install gems -
it will try to upgrade every single gem in your bundle.
That's usually a disaster unless you really meant to do it.
The update command is for when gems you use has been updated,
and you want your bundle to have the newest version that your
Gemfile
will allow
[~/ruby/faye]$ bundle help outdated
Usage:
bundle outdated [GEM]
Options:
[--pre=Check for newer pre-release gems]
[--source=Check against a specific source]
[--local=Do not attempt to fetch gems remotely and use the gem cache instead]
[--no-color=Disable colorization in output]
-V, [--verbose=Enable verbose output mode]
Description:
Outdated lists the names and versions of gems that have a newer version
available in the given source. Calling outdated with [GEM [GEM]]
will only check for newer versions of the given gems. Prerelease gems
are ignored by default. If your gems are up to date, Bundler will exit
with a status of 0. Otherwise, it will exit 1.
[~/ruby/faye]$ ls -l Gemfile* -rw-r--r-- 1 casiano staff 267 15 nov 18:01 Gemfile -rw-r--r-- 1 casiano staff 2373 15 nov 18:02 Gemfile.lock [~/ruby/faye]$ bundle outdated Fetching gem metadata from https://rubygems.org/......... Fetching gem metadata from https://rubygems.org/.. Resolving dependencies... Outdated gems included in the bundle: * em-websocket (0.5.0 > 0.3.8) * rainbows (4.5.0 > 4.4.3)
Bundler uses your Gemfile
to create what is technically called a dependency graph,
where there are many gems that have various dependencies on eachother.
It can be pretty cool to see that dependency graph drawn as a literal graph, and that's what the bundle viz command does.
You need to install GraphViz and the ruby-graphviz gem:
$ brew install graphviz # for mac os X. apt-get for Linux $ gem install ruby-graphviz $ bundle vizOnce you've done that, though, you get a pretty picture that's a lot of fun to look at. Here's the graph for a Gemfile:
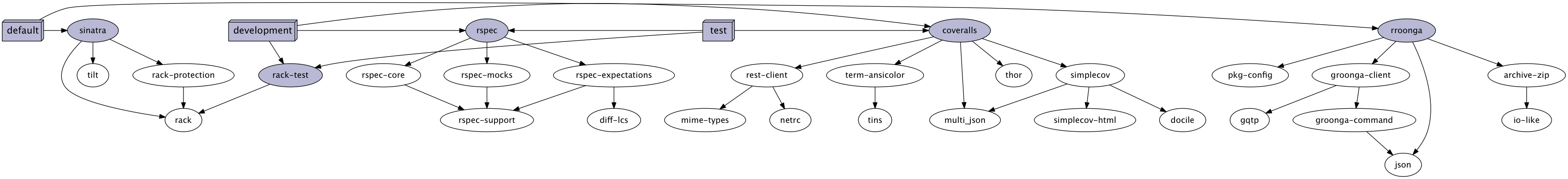
En violeta las que forman parte del Gemfile.
Los nodos cuadrados son entornos.
Gemnasium https://gemnasium.com is a service that learns your gem dependencies, listens for new versions of those gems and notifies you when they’re released.
Gemnasium sends you an email whenever a new version is released for a gem that you use. You can turn off notifications for particular gems or for entire repositories, or choose to receive them in a digest email on a daily or weekly basis.
Gemnasium represents the statuses of your dependencies with three colors:
Gemnasium looks the Gemfile.lock files. If your repository has one, Gemnasium will use it. They’re informational and easily parsed with a little help from Bundler.
Unfortunately, it’s not always wise to commit your Gemfile.lock. In those cases, Gemnasium looks for a Gemfile instead.
If all else fails, Gemnasium looks for a gemspec file in your repository’s root directory.
If any of these files exists, Gemnasium parses them to determine your repository’s gem dependencies.